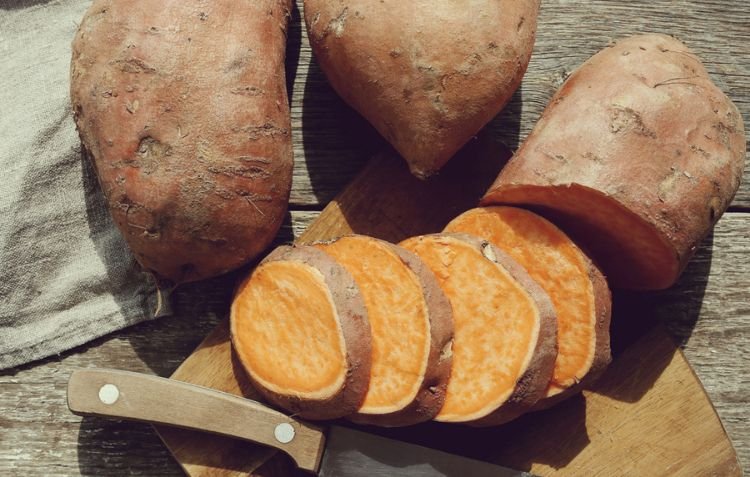
Sweet potatoes have traveled an incredible journey before becoming a beloved staple in Texas. Originally cultivated over 5,000 years ago in South America, these nutrient-rich tubers crossed continents, adapting to different climates and cuisines along the way. But how far did sweet potatoes travel to Texas? The answer traces back to early explorers, trade routes, and agricultural innovations that helped sweet potatoes establish deep roots in Texan soil.
Today, Texas is known for producing high-quality sweet potatoes, playing a crucial role in the state’s agriculture and culinary traditions. From classic Southern recipes to modern fusion dishes, these vibrant tubers continue to shape Texan cuisine. But their journey was far from simple. How did sweet potatoes survive long voyages, and what made Texas an ideal place for cultivation?
In this article, we’ll uncover the fascinating history, migration, and impact of sweet potatoes in Texas. Keep reading to explore their incredible voyage!
Table of Contents
ToggleThe Origins of the Sweet Potato
Sweet potatoes have a long and fascinating history, with their origins deeply rooted in the tropical regions of South America. These hardy, nutrient-dense tubers have been a staple food for indigenous civilizations for thousands of years, offering sustenance and versatility in various culinary practices.
Native Roots in South America
Sweet potatoes (Ipomoea batatas) are believed to have first been cultivated in present-day Ecuador and Peru over 5,000 years ago. Archaeological evidence suggests that indigenous communities grew these tubers due to their adaptability to different climates and soil types. Rich in vitamins, fiber, and antioxidants, sweet potatoes provided an essential food source in pre-Columbian societies.
Early Cultivation and Uses
Indigenous civilizations, including the Inca and other Andean cultures, developed advanced farming techniques to maximize sweet potato production. They consumed them roasted, boiled, or mashed and even fermented them for preservation. Sweet potatoes were not just food but also held cultural significance, playing a role in rituals and medicinal practices. These early agricultural advancements set the stage for the tuber’s eventual global journey.
The Sweet Potato’s Global Journey
The journey of the sweet potato from South America to the rest of the world is a story of exploration, trade, and adaptation. Over centuries, this humble crop spread across continents, influencing diverse cuisines and agricultural practices.
Introduction to Europe
In 1492, Christopher Columbus encountered sweet potatoes during his travels to the Americas. Recognizing their nutritional value and unique taste, he brought them back to Spain, where they quickly gained popularity. Spanish and Portuguese explorers further promoted their cultivation, leading to the sweet potato’s widespread use in European diets by the 16th century.
Spread to Africa and Asia
European traders played a crucial role in introducing sweet potatoes to Africa and Asia. The Portuguese, in particular, carried the crop along their trade routes, planting it in regions such as West Africa, India, and China. Sweet potatoes thrived in these areas due to their resilience to drought and poor soil conditions. Over time, they became a staple food in many cultures, often replacing traditional crops during periods of famine.
Arrival in Polynesia
One of the most intriguing aspects of the sweet potato’s history is its presence in Polynesia long before European contact. Some theories suggest that Polynesian voyagers may have traveled to South America and brought sweet potatoes back with them. Others propose that ocean currents carried the seeds across the Pacific. Regardless of how they arrived, sweet potatoes became an integral part of Polynesian agriculture and cuisine, further expanding their global reach.
Introduction of Sweet Potatoes to North America
The arrival of sweet potatoes in North America marked a significant moment in agricultural history. Over time, they became deeply embedded in the region’s farming, culinary traditions, and cultural identity.
Early Adoption in the Southern United States
Sweet potatoes were introduced to the Southern United States in the early colonial period, likely brought by European settlers and African slaves. Due to their adaptability to warm climates and poor soil conditions, they quickly became a staple crop, particularly in states like Virginia, Georgia, and the Carolinas.
During the Revolutionary War, sweet potatoes served as a crucial food source for soldiers and civilians alike, offering a reliable alternative when other crops were scarce. Their long shelf life and nutritional benefits made them an essential survival food, further cementing their role in Southern agriculture.
Cultural Significance Among African American Communities
Sweet potatoes hold deep cultural significance within African American communities. Enslaved Africans, who were already familiar with similar root vegetables from their native lands, embraced sweet potatoes and incorporated them into their cooking. Over generations, they became a foundational ingredient in soul food, appearing in dishes like sweet potato pie, candied yams, and casseroles.
These traditions continue today, with sweet potatoes symbolizing resilience, heritage, and community in African American cuisine.
The Journey to Texas
Sweet potatoes made their way to Texas through a blend of Spanish exploration, settler farming, and agricultural innovation. Over the centuries, they became a key component of Texan cuisine and farming traditions.
Spanish Influence in the 16th Century
The earliest introduction of sweet potatoes to Texas can be traced back to Spanish explorers in the 16th century. As they traveled through the Gulf Coast and into present-day Texas, they brought sweet potatoes from their Caribbean and Central American colonies.
These explorers, including Álvar Núñez Cabeza de Vaca, likely introduced the crop to indigenous communities, who incorporated it into their diets. Spanish missions and settlements later played a crucial role in spreading sweet potato cultivation, particularly in areas with warm, fertile land.
Adoption by Anglo-American Settlers
In the 19th century, Anglo-American settlers further integrated sweet potatoes into Texas agriculture. Many of these settlers migrated from the Southern U.S., where sweet potatoes were already a dietary staple. They established farms in East and Central Texas, taking advantage of the region’s climate to grow large quantities of the crop. Over time, sweet potatoes became a common ingredient in Texan home cooking, appearing in everything from roasted side dishes to desserts.
Development of Texan Sweet Potato Varieties
As sweet potatoes became more widespread in Texas, farmers developed unique cultivation methods and adapted different varieties to local conditions. Today, Texas is known for producing high-quality sweet potatoes, particularly in regions like Van Zandt County, which hosts an annual Sweet Potato Festival. Texan farmers have refined growing techniques to improve yield, texture, and flavor, ensuring the state remains a significant player in U.S. sweet potato production.
Sweet Potatoes in Modern Texas
Sweet potatoes remain an integral part of Texas agriculture and cuisine, contributing to both the state’s economy and culinary heritage. From large-scale farming to innovative recipes, their influence continues to grow.
Current Production and Economic Impact
Texas ranks among the top sweet potato-producing states in the U.S., with Van Zandt County being a major hub. Farmers cultivate thousands of acres annually, benefiting from Texas’s warm climate and sandy soils. According to the USDA, sweet potato production in Texas generates millions of dollars in revenue, supporting local farmers and agribusinesses. The demand for sweet potatoes has increased in recent years due to their health benefits, leading to expanded cultivation and distribution across grocery stores, farmers’ markets, and restaurants.
Culinary Traditions and Innovations
In Texas, sweet potatoes are a beloved ingredient in both traditional and contemporary dishes. Classic Southern recipes like sweet potato pie and candied yams remain staples, especially during holidays. However, modern chefs have embraced them in new ways, incorporating them into tacos, barbecue sides, fries, and even plant-based meals. With the rise of farm-to-table dining and health-conscious eating, sweet potatoes continue to inspire innovative culinary creations across Texas.
Conclusion
The journey of the sweet potato—from its origins in South America to its establishment in Texas—reflects its remarkable adaptability and cultural significance. Introduced by Spanish explorers and embraced by settlers, sweet potatoes became a key crop in Texan agriculture. Over the centuries, they evolved from a survival food into a cherished staple in home kitchens and restaurants alike.
Today, Texas continues to play a vital role in sweet potato cultivation, contributing to both the state’s economy and its diverse culinary landscape. Whether featured in time-honored family recipes or reimagined in modern cuisine, sweet potatoes remain a symbol of resilience, tradition, and innovation. Their lasting presence in Texan food culture underscores their importance, ensuring that future generations will continue to enjoy and celebrate this versatile root vegetable.
If you enjoyed learning about the journey of sweet potatoes to Texas, explore more insightful articles on history, food, and culture at The Fast Upload. Stay informed with engaging and well-researched content!
FAQs
When is the best time to plant sweet potatoes in Texas?
In Central Texas, it’s ideal to plant sweet potatoes in April, as they thrive in warm temperatures and well-drained soils.
How long does it take for sweet potatoes to mature?
Sweet potatoes typically mature 90 to 120 days after planting. It’s recommended to stop watering 2 to 3 weeks before harvest to allow the tubers to mature properly.
What are the main sweet potato varieties grown in Texas?
In Texas, the ‘Beauregard’ variety is predominantly grown due to its high yield and quality. Other varieties include ‘Centennial’ and ‘Jewel’.
How significant is sweet potato farming to Texas’s economy?
Sweet potato farming contributes approximately $14 million annually to Texas’s economy, with the majority of production concentrated in the eastern part of the state, especially near Van Zandt County.
How are sweet potatoes used in Texan cuisine?
Sweet potatoes are versatile in Texan cuisine, featuring in traditional dishes like sweet potato pie and candied yams, as well as modern recipes such as sweet potato fries and roasted sweet potatoes.












